Manifold
Manifold are essential for studying systems that can be observed only locally. Therefore it useful tool for tasks of observation, optimal path finding and generalization of knowledge
Concept of manifold may seem difficult at first glance, due it’s abstract definition.
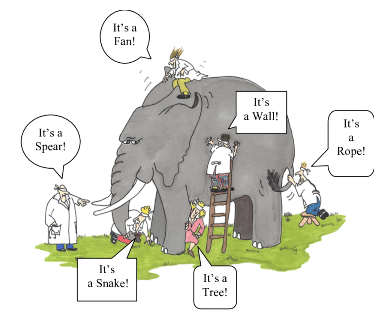
Blind man and elephant
Once upon a time, in a small village nestled between rolling hills and lush forests, there lived six blind men. Each of them was curious and eager to explore the world around them despite their inability to see. One day, they heard tales of a magnificent creature called an elephant that had arrived in their village. Excited to experience something new, they decided to seek out the elephant.
With their canes tapping the ground, the blind men made their way to where the elephant was said to be. As they approached, they could feel the ground rumbling beneath their feet, and the air was filled with the sound of trumpeting.
The first blind man, reaching out his hands, touched the elephant’s side. “Ah,” he exclaimed, “the elephant is like a sturdy wall, strong and immovable!”
The second blind man, feeling the elephant’s trunk, disagreed. “No, it’s not like a wall at all,” he said. “The elephant is long and flexible, like a snake.”
The third blind man, holding onto the elephant’s tusk, chimed in, “Neither of you is correct. The elephant is hard and smooth, sharp like a spear.”
The fourth blind man, wrapping his arms around one of the elephant’s legs, argued, “You’re all mistaken. The elephant is thick and cylindrical, like a tree trunk.”
The fifth blind man, feeling the elephant’s ear, chuckled. “You’re all only partly right,” he said. “The elephant is wide and flat, like a giant fan.”
The sixth blind man, who had reached up to touch the elephant’s tail, shook his head. “No, no, no,” he said. “The elephant is thin and wiry, like a rope.”
As the blind men continued to discuss and debate what they had felt, a wise old villager passing by overheard their conversation. With a gentle smile, he approached them and said, “My friends, you are all correct in your own way. The elephant is indeed all the things you have described and more. Each of you has touched just one part of the elephant, but none of you can fully comprehend its entirety without considering the perspectives of others.”
Realizing the wisdom in the old man’s words, the blind men nodded in understanding. From that day on, they learned to appreciate the value of different perspectives and understood that the truth often lies in the combination of them all. And as they continued their journey through life, they embraced the diversity of experiences and opinions, knowing that it enriched their understanding of the world around them.
 |
|---|
| Rigid body lattice |
So it said, manifold is a mathematical concept with object which can sensed only locally.
Introduction
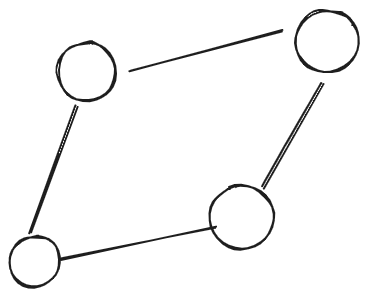
We’ll start graph, which serves for same goal as manifold in discrete cases. Recall graph is just a collection of edges and
 |
|---|
| Graph is just a bundle of node and edges |
Due to the one of the most important problems, how to find something. Suppose you are foreign city and you want to find supermarket.
 |
|---|
| Where I can buy food? |
Let’s find out it iteratively by visiting nearest streets. For that we use bread-search algorithm.
 |
|---|
| Depth search by slama.dev. Flash mean observation. Blue node candidates. |
ou walk from your starting point - home and look around. When you’ll observe supermarket. you’’ build optimal path. In manifold studying it’s called geodesics.
Elucidating manifold
Manifold are
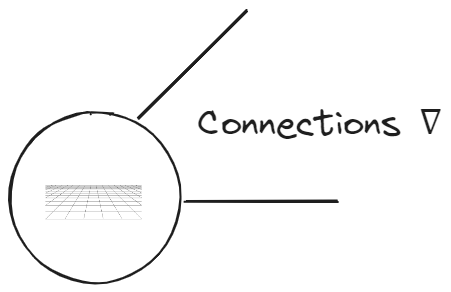
Edges are named connection and defined via Cristofel $K$ and Levi-Civitia $\nabla$ symbols.
 |
|---|
| Nodes now Euclidian surface, edges Levi-Civitia symbols |
As we understand from discrete representation we need to know to main things, how to measure distance for geodesics. For that we need metric and
 |
|---|
| Tangent space |
Metric is a way of measuring distance between vectors in tangent space. Most common is just an angle.
Locally manifold are just normal euclidian. It’s like graph node stores in it’s state.
Locally euclidian
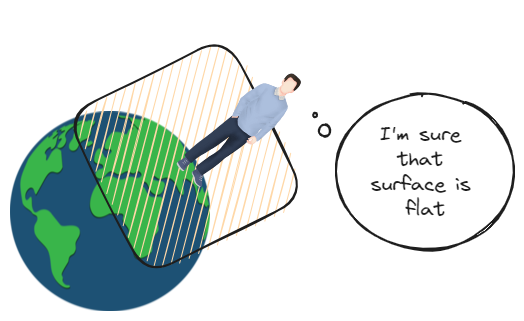
Recall that earth was believed to be flat for many ears. It took tremendous time for brightest minds to elucidate from observations, that surface is only locally flat, but in whole spherical
 |
|---|
| *Manifolds are locally * |
For working we use atlases. It’s a whole graph of a world.
Graph can be different
Maps, pushforward and pullback
Yet not all manifold are convenient to work about, some of them are too curly or don’t proper way to measure distance on them.
 |
|---|
| Tangent space |
Easiest example is polar coordinate system
therefore we can choose a better representation. Something more flat, which allows to better approximate distances and metrics
Connection between manifold of studying and better presentation is given map by map $f$.
 |
|---|
| Tangent space |
We require from this map to be revertible for
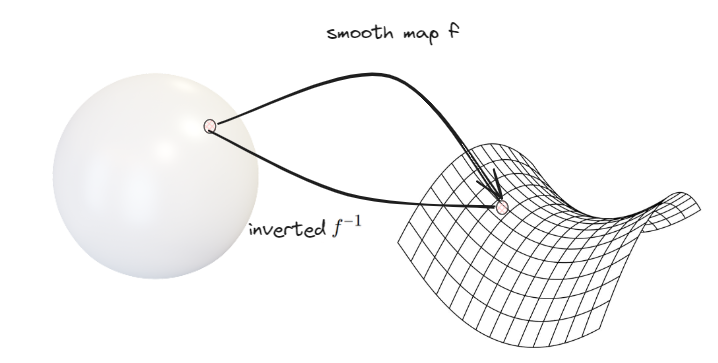 |
|---|
| Smooth map to more flat space |
For translation vector from tangent space we have pushforward transformations
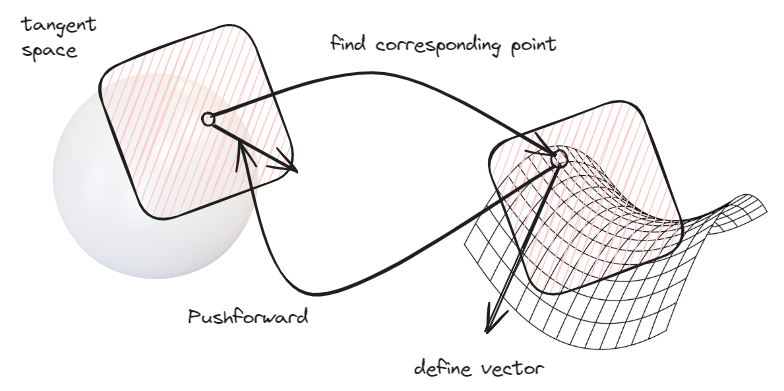 |
|---|
| Pushforward |
Vector can change significantly after pushforawd operation: rotate and scales.
Exact transformation is given via pushforward Jacobian in exact point.
\[J = \begin{bmatrix} \frac{\partial u_1}{\partial x_1} & \frac{\partial u_1}{\partial x_2} & \frac{\partial u_1}{\partial x_3} \\[1ex] % <-- 1ex more space between rows of matrix \frac{\partial u_2}{\partial x_1} & \frac{\partial u_2}{\partial x_2} & \frac{\partial u_2}{\partial x_3} \\[1ex] \frac{\partial u_3}{\partial x_1} & \frac{\partial u_3}{\partial x_2} & \frac{\partial u_3}{\partial x_3} \end{bmatrix}\]In manifold studying they will bring atlas. Similarity comes fact.
Metric works effectively the same, but map is called pullback.
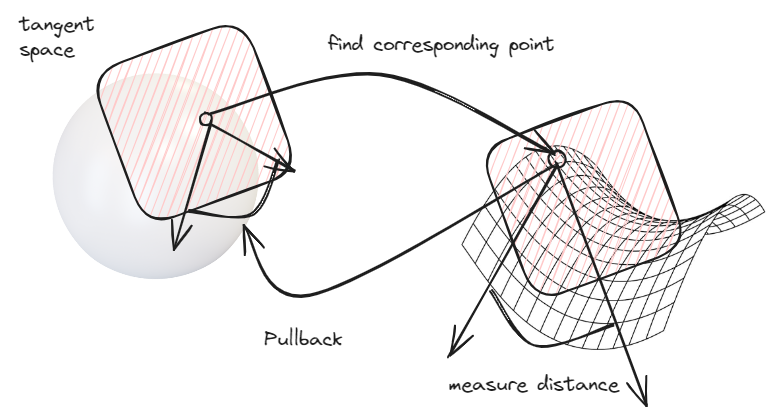 |
|---|
| Pushforward |
Finally, for metric needed for measuring
Pushback properies
There are some essential properties that we want to preserve
When we send structures to like faces we wand them to keep face
More formally it’s named called equivariance
|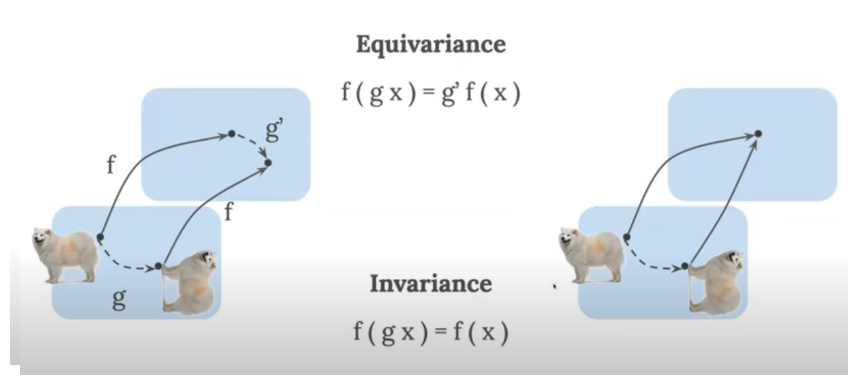 | |:–:| | *Rotation in both spaces should be seamless. Picture link * | Moreover we want to preserve similarity, which comes from angles between vectors. Such transformations are named conformal
| |:–:| | *Rotation in both spaces should be seamless. Picture link * | Moreover we want to preserve similarity, which comes from angles between vectors. Such transformations are named conformal
For approxiation of Jacobian we choose sum of eigenvectors with biggest eigenvalues
It measures how small changes of one basis affects others. That’s it. Pairwise interaction between basis vectors.
We need to choose vectors that preserve correlations between input features.
Recall that eigenvectors are vector preserved under transformations
\[\]Superficial simmilarity and superposition
So than manifold
Learn more
-
An Intuitive Introduction to Manifolds & Topology, Part I. Another introduction from different angle
-
Visit this fun video [MATH ONLY] Non-Euclidean Therapy for AI Trauma [Analog Archives] to build manifold intuition with exciting story of diffusion net Alice.
-
Geomstats. Python library with rigorous introduction to manifold studying
-
The Lie Derivative for Measuring Learned Equivariance https://arxiv.org/abs/2210.02984
-
3-MANIFOLDS, KNOTS, AND HOMOLOGY 3-SPHERES https://ishanina.github.io/Academic%20Projects/3-Manifolds%20Knots%20and%20Homology%203-Spheres%20Junior%20Paper/3-Manifolds_Knots_and_Homology_3-Spheres_Junior_Paper.html
Great seminar on geometric learning AMMI Seminar - Geometric Deep Learning and Reinforcement Learning (2021)